g7 g8 g9 g10 g11 fr4 fr5 introduction and differences
2024-06-28 14:34 | By: ZTELEC-www.ztelecgroup.com | 77click
The differences between G7, G8, G9, G10, G11, FR4, and FR-5 materials are primarily based on their composition, temperature resistance, and mechanical properties. Here’s a brief overview:

G7 epoxy board
Epoxy board G7, also known as G7 Glass Silicone Laminate, is a high-performance material made from a woven fiberglass substrate and silicone resin. It’s designed to meet the NEMA G-7 and MIL-I-24768/17 standards, offering excellent mechanical and electrical characteristics, along with high heat and superior arc resistance. Here are some key properties of G7:
Specific gravity: 1.78.
Tensile strength: 45,000 psi.
Flexural strength: 25,000 psi.
Shear strength: 17,000 psi.
Bond strength: 900 psi.
Hardness (Mohs Scale): 105.
Flammability rating: 94V-0.
Maximum operating temperature: 220°C (428°F).
Water absorption (24 hours): 0.20.
G7 is particularly valued for its ability to maintain strength at higher temperatures, up to 200°C, and its low-smoke evolution while meeting Class H insulation requirements. It works well in both wet and dry conditions and is ideal for applications requiring solid mechanical and electrical properties.
Typical uses for G7 include:
Arc barriers and plates
Insulation in heating systems and appliances
Terminal boards
Spacers, sleeves, and wedges
Telecom equipment
Transformers
Due to its exceptional electrical resistance and stability at elevated temperatures, G7 is perfect for constructing tips inside welding guns and is also self-extinguishing and stable in high humidity, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial and electrical applications.
G8 epoxy board
they are composite materials made from woven fiberglass cloth and an epoxy resin binder. They are known for their high strength, low moisture absorption, and superior electrical properties. Epoxy boards are commonly used in electronic and electrical applications, such as printed circuit boards (PCBs), due to their flame retardant properties and durability.it would be best to consult the manufacturer’s datasheet or contact the supplier for detailed information on that particular product.
G9 epoxy board
Epoxy board G9, also known as G9 Melamine, is a type of thermoset laminate made from woven glass fabric and melamine resin. It’s recognized for its excellent mechanical properties and resistance to harsh conditions. Here are some notable features of G9 epoxy board:
Tensile strength: 70,000 psi.
Compressive strength: 39,000 psi.
Flexural Strength: 55,000 psi.
Specific gravity: 1.85.
Bond strength: 1,900 psi.
Shear strength: 18,000 psi.
Hardness (M Scale): 115.
Flammability rating: 94V-0.
Water absorption (24 hours): 0.60.
Izod impact strength at 49°C: 12.50.
G9 has excellent heat resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 284 degrees Fahrenheit (140 degrees Celsius)1. It maintains its electrical insulative strength even in humid or wet conditions, making it suitable for applications that require electrical insulation and good mechanical strength under such conditions.
Common uses for G9 epoxy board include:
Arc barriers
Armature for insulation
Specialty terminal blocks
Switchboard panels
Switch mounts
Circuit breaker components
Motor wedges
Terminal boards
G10 epoxy board:
Epoxy board G10 is a high-pressure fiberglass laminate, which is a composite material made of glass fabric and electrical grade epoxy resin. It’s known for its exceptional strength, stiffness, and outstanding electrical properties. Here are some key characteristics of G10:
Flame retardant: It’s designed to be self-extinguishing.
Strong and stiff: Provides excellent mechanical stability.
Dimensionally stable: Maintains its shape and size over a wide range of temperatures and humidities.
Outstanding electrical properties: Excellent insulator for electrical and electronic applications.
Creep resistance: Maintains its mechanical properties under continuous load.
G10 is widely used in applications such as:
Printed circuit boards (PCBs)
Insulators for electromechanical devices
Jigs and fixtures
High strength composite parts
The material is also known for its low coefficient of thermal expansion, which means it doesn’t expand or contract much with temperature changes. This makes it ideal for precision parts where dimensional stability is crucial.
G11 epoxy board:
Epoxy board G11 is a high-temperature glass epoxy laminate that is similar to G10 but with enhanced properties to withstand higher temperatures. Here are some notable properties of G11:
Tensile strength: 63,000 psi.
Compressive strength: 37,000 psi.
Flexural strength: 75,000 psi.
Bond strength: 2,200 psi.
Shear strength: 22,000 psi.
Hardness (M scale): 112.
Specific gravity: 1.82.
Flammability rating: 94HB.
Maximum temperature: 180°C (356°F).
Water absorption (24 hours): 0.20.
Izod impact strength at 49°C: 12.00.
G11 is designed for applications that require a durable material that can maintain its mechanical and insulative strength in a range of conditions, including high temperatures. It’s suitable for use in both wet and dry environments and can withstand temperatures up to 180 degrees Celsius, depending on the grade.
Common applications for G11 include aerospace equipment, antenna insulators, cryogenic insulation, circuit board holders, end plates, electrical equipment, medical diagnostic equipment, rocket cases, solder frames, and more.
G11 can be machined using standard cutting tools and can also be wound into tubes using convolute or filament winding methods. Its benefits include chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, high impact strength, high dielectric strength, high tensile strength, high flexural strength, radiation resistance, low cold flow, low dissipation factor, dimensional stability, and cryogenic serviceability.

FR4 epoxy board:
FR4, short for Flame Retardant 4, is a grade designation for the epoxy fiberglass cloth used as the base material in most types of printed circuit boards (PCBs). It’s chosen for its high temperature tolerance, rigidity, and excellent electrical insulating properties. Here are some key properties of FR4:
Composition: It’s composed of woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder that is flame resistant (self-extinguishing).
Flame Retardancy: The “FR” stands for “flame retardant,” and it complies with the UL94V-0 standard, which is crucial for materials used in electronic applications requiring flame retardancy.
Mechanical Strength: FR4 has good strength to weight ratios, retaining its high mechanical values and electrical insulating qualities in both dry and humid conditions.
Thermal Properties: It has a temperature index of 140°C (284°F) and exhibits low thermal conductivity, with through-plane conductivity of 0.29 W/(m·K) and in-plane conductivity of 0.81 W/(m·K).
Electrical Insulation: The epoxy resin ensures excellent insulation, preventing electrical shorts and maintaining signal integrity within the PCB.
Water Absorption: FR4 has near zero water absorption, which is essential for maintaining its insulating properties in various environments.
FR4 is widely used in the electronics industry, especially for PCBs, due to these properties. It’s also used in communication devices, computer hardware, consumer electronics, industrial electronics, and medical devices3. When choosing FR4 for your design, consider factors like board thickness, dielectric properties, and thermal performance to ensure it meets the specific needs of your application
FR-5 epoxy board:
FR5 is a high-grade epoxy laminate that is similar to FR4 but designed for more demanding applications, particularly where higher temperatures are involved. Here are some key properties of FR5:
Specific Gravity/Density: 1.85 g/cm³.
Water Absorption: Less than 0.10%.
Temperature Index: 180°C (356°F).
Rockwell Hardness: 115 M scale.
Bond Strength: Greater than 2,200 lbs (1,000 kgs).
Flexural Strength: Greater than 75,000 psi (520 MPa).
Compressive Strength: Greater than 65,000 psi (448 MPa).
Dielectric Breakdown: Greater than 50 kV.
Permittivity: 4.8.
Dissipation Factor: 0.017.
FR5 is known for its extremely high mechanical strength at elevated temperatures and maintains good properties in both dry and humid conditions. It’s often used in electrical equipment, antenna isolators, circuit board holders, aerospace test boards, end plates, and solder frames.
The material’s high glass transition temperature (Tg) of 170-180°C makes it suitable for multilayer PCBs with higher layer counts, especially in automotive applications where improved Tg is crucial. Its low moisture absorption and good chemical resistance make it a reliable choice for various industrial applications.
Data of various epoxy plates
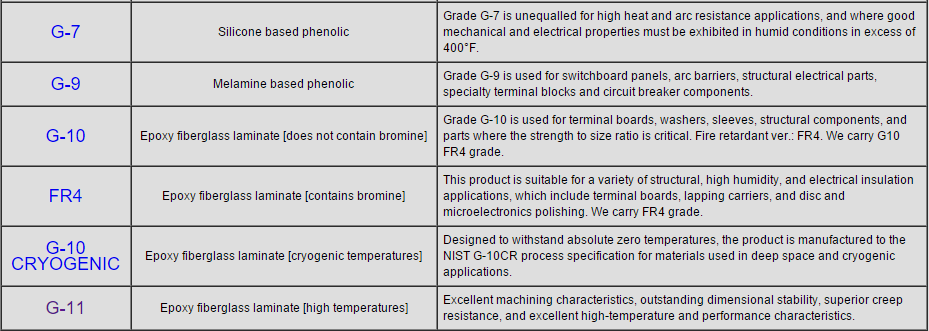
Epoxy Plate Summary
The G7, G8, and G9 grades are less commonly discussed but are part of the same family of glass-reinforced epoxy laminates, each with unique properties suitable for specific applications. For instance, G7 is a silicone glass laminate with good heat and arc resistance, while G8 and G9 are variations with different resin systems and temperature ratings.
These materials are used in a variety of applications, including electrical insulation, printed circuit boards, aerospace components, and more. The choice between these materials typically depends on the specific requirements of the application, particularly concerning thermal performance, mechanical strength, and environmental resistance.
For detailed specifications and to choose the right material for your application, it’s best to consult with a materials specialist or refer to the manufacturer’s datasheets. If you need further assistance, feel free contact us!
tags:insulation failure transformertransformer short circuittransformer overheatingtransformer overloadtransformer maintenance
- more+releated article
- 2026-01-04Common Power Transformer Faults: Causes, Solut
- 2025-12-312026 New Year Holiday Notice
- 2025-12-31Operation, Maintenance, and Service Life Manag
- 2025-12-30How to Select a 100 kVA–500 kVA Distribution
- 2025-12-29The Impact of NHN NMN Composite Insulation on
- 2025-12-26Practical Application of GPO-3 Insulation Boar
- 2025-12-2510kV Transformer Replacement Timeline: Install
- 2025-12-25Low Smoke EN45545 GPO3 UPGM203 Laminated Board
- 2025-12-24Merry Christmas — ZTelecgroup Christmas Cele
- 2025-12-24How to Select a Suitable 50kVA–500kVA Distri





