Single Phase Transformer Connections Explained
In modern power systems, single-phase distribution transformers serve as key devices for the transmission and distribution of electrical energy, responsible for converting high-voltage electrical energy into low-voltage electrical energy. As the demand for electricity continues to grow, higher requirements are placed on the performance and connection methods of distribution transformers. This article will provide a detailed explanation of the basic working principles, main types, connection methods, and applications of single-phase distribution transformers, aiming to guide the safe and efficient operation of power systems.
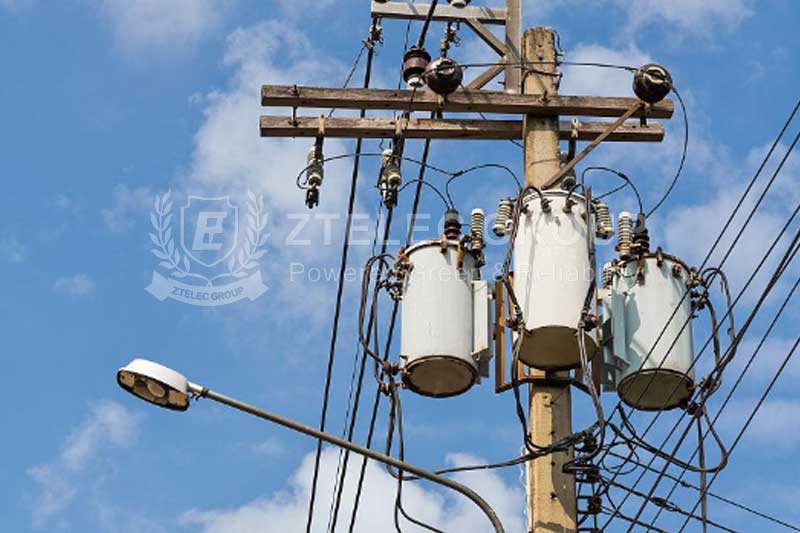

I. Basic Principles of Single-Phase Distribution Transformers
A single-phase distribution transformer primarily consists of a core, primary winding, secondary winding, and oil tank. Its working principle is based on the law of electromagnetic induction. When alternating current flows through the primary winding, it generates an alternating magnetic field in the core, which induces a voltage in the secondary winding. According to the characteristics of the transformer, the turns ratio between the primary and secondary windings determines the voltage transformation ratio.
II. Classification of Single-Phase Distribution Transformers
Single-phase distribution transformers can be classified according to different criteria, mainly including the following types:
1. Classification by Cooling Method:
Oil-Immersed Transformers: This type of transformer uses insulating oil for cooling and insulation, and is commonly used outdoors and in high-power applications.
Dry-Type Transformers: These use air as the cooling medium and are usually employed in indoor environments, offering high safety and easy maintenance.
2. Classification by Winding Connection Method:
Star (Y) Connection: This connection can provide a neutral point and is suitable for substations and distribution networks. The star connection has a minimal impact on the power quality received by users.
Delta (Δ) Connection: Suitable for supplying high-power equipment, this connection can provide relatively high short-circuit currents.
III. Connection Methods for Single-Phase Distribution Transformers
In practical applications, the connection method of single-phase distribution transformers is a significant factor determining their performance. The following are several common connection methods:
1. Star Connection:
In a star connection, one end of the three-phase windings is connected to a common point (neutral point), while the other ends are connected to three phase lines. The advantage of this connection method is that it can balance the load across all phases, reduce phase-to-phase voltage, and enhance the stability of the system.
2. Delta Connection:
The delta connection typically does not have a neutral point, and the three-phase windings are connected in sequence to form a closed loop. This connection method is suitable for high-power and industrial equipment, possessing a high capacity to withstand short-circuits, yet it has poor adaptability to unbalanced loads.
3. Series and Parallel Connection of Single-Phase Transformers:
In certain cases, multiple single-phase transformers can be connected in series or in parallel to achieve the desired voltage and power. For instance, connecting two single-phase transformers in series can raise the voltage, while a parallel connection can increase the power supply capacity.
IV. Application Areas of Single-Phase Distribution Transformers
Single-phase distribution transformers are widely used in various electrical distribution systems, particularly in residential areas, small shops, and rural power networks. Their primary application areas include:
1. Residential Power Supply: In residential areas, single-phase distribution transformers are typically used to reduce the high voltage from the supply network to 220V, to meet the needs of household electrical appliances.
2. Small Commercial Facilities: Many small shops and office buildings rely on single-phase transformers for a stable power supply to support daily operations.
3. Agriculture and Rural Power Networks: In rural areas, single-phase distribution transformers are an essential component of the power supply network, providing electricity for irrigation, livestock farming, and other agricultural needs.
V. Connection Considerations
When connecting single-phase distribution transformers, several considerations should be emphasized:
1. Load Balancing: Ensure that the connected loads are evenly distributed among phases to prevent damage caused by overload in any single phase.
2. Grounding Requirements: The neutral point of the transformer should be effectively grounded to avoid voltage fluctuations and equipment damage due to faults.
3. Protection of the Distribution System: Install appropriate protective devices such as circuit breakers and fuses to ensure safe operation of the transformer.
4. Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain the transformer to eliminate potential hazards and ensure stable long-term operation.
Single-phase distribution transformers hold an irreplaceable position in power systems. By paying attention to connection methods, load balancing, and safety issues during connection and use, the stability and reliability of the power system can be significantly enhanced. To adapt to the ever-changing electricity demand, more efficient and smarter transformer technologies may emerge in the future, driving the ongoing development and innovation of the power industry.
- more+releated article
- 2026-01-04Common Power Transformer Faults: Causes, Solut
- 2025-12-312026 New Year Holiday Notice
- 2025-12-31Operation, Maintenance, and Service Life Manag
- 2025-12-30How to Select a 100 kVA–500 kVA Distribution
- 2025-12-29The Impact of NHN NMN Composite Insulation on
- 2025-12-26Practical Application of GPO-3 Insulation Boar
- 2025-12-2510kV Transformer Replacement Timeline: Install
- 2025-12-25Low Smoke EN45545 GPO3 UPGM203 Laminated Board
- 2025-12-24Merry Christmas — ZTelecgroup Christmas Cele
- 2025-12-24How to Select a Suitable 50kVA–500kVA Distri





