Unveiling the Differences Between a Transformers and a Switching Power Supplies
Power transmission is the cornerstone of modern society's operations, and in this process, transformers and switching power supplies serve as core devices, each playing an indispensable role. Although both devices perform the function of voltage and current transformation within power systems, their working principles, application scenarios, and technical characteristics significantly differ. Understanding these differences helps us gain deeper insights into the mysteries of power transmission.
What is a transformer
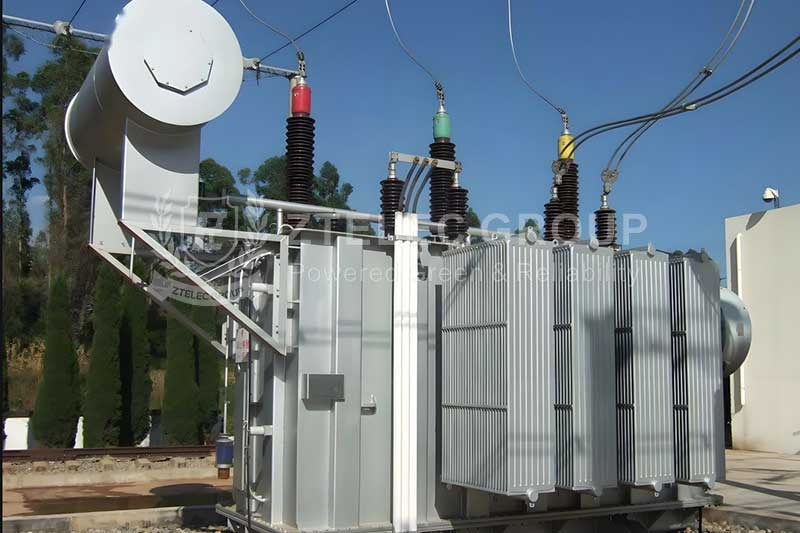
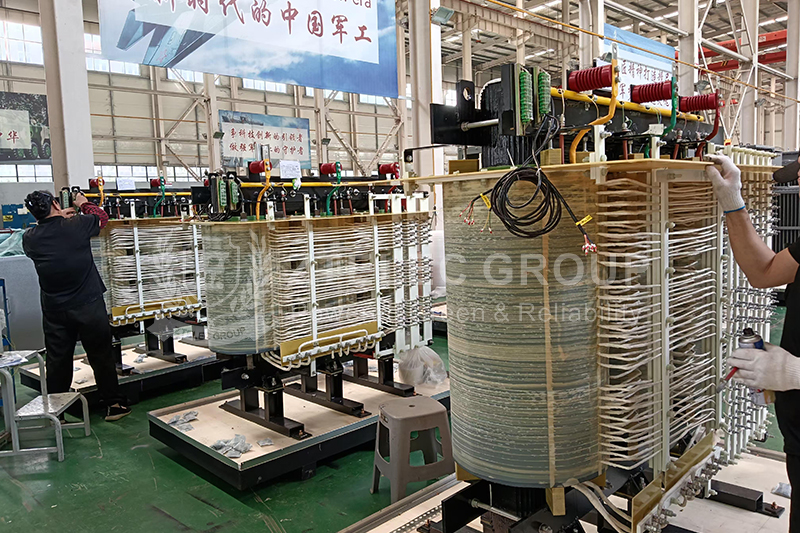
A transformer is a device that converts voltage using the principle of electromagnetic induction. It consists of two windings (primary winding and secondary winding) with an iron core that enhances the strength of the magnetic field, thus effectively transmitting energy. The working principle of a transformer is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction; when alternating current flows through the primary winding, it generates an alternating magnetic field, inducing voltage in the secondary winding. The main function of a transformer is to step up or step down voltage to meet different power transmission requirements.
Applications of Transformers
Transformers are widely used in power transmission and distribution systems, especially during the transmission of electricity from power plants to consumers. By increasing voltage, transformers can reduce energy losses during transmission. Additionally, transformers facilitate the conversion between various voltage levels at different nodes in the power grid, ensuring efficient delivery of electric energy to users.
Basic Concept of Switching Power Supplies
A switching power supply (SPS) is a power conversion device that utilizes switching components (such as transistors) to periodically switch on and off to control current and voltage. It employs high-frequency switching technology to reduce energy losses while achieving voltage step-up, step-down, and stabilization. The operation of a switching power supply typically includes several steps: input rectification, filtering, switch control, transformation, and output filtering.
Advantages of Switching Power Supplies
Compared to traditional linear power supplies, switching power supplies offer significant advantages in size, efficiency, and application range. Due to their high-frequency operation, switching power supplies can achieve efficient energy conversion in a smaller space, reducing heat generated by current consumption. Moreover, their flexibility and adjustability make switching power supplies widely applicable in electronic devices, communication equipment, computers, and various consumer electronic products.

Key Differences Between Transformers and Switching Power Supplies
1. Working Principle
Transformers operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, primarily relying on alternating current, while switching power supplies utilize switching modulation technology to achieve energy conversion by rapidly toggling the state of the switches. This leads to significant differences in efficiency and application scenarios between the two.
2. Energy Efficiency and Losses
Transformers usually maintain high efficiency across a broad range of loads, but their energy consumption can be relatively high under low-load conditions. In contrast, switching power supplies can maintain high energy efficiency under varying load conditions through high-frequency switch operations, making them especially suitable for applications with higher energy efficiency requirements.
3. Size and Weight
Transformers typically occupy larger volumes and weights, especially in high-power transmission applications. On the other hand, switching power supplies can achieve smaller sizes and lighter weights under the same power conditions due to their high-frequency characteristics, making them more advantageous for mobile devices and compact electronic products.
4. Cost and Technical Complexity
Generally, transformers have lower manufacturing costs and simpler structures. Conversely, switching power supplies have higher production and maintenance costs due to their complex circuit designs and control mechanisms. However, their versatile applications and efficiency often offset their cost disadvantages.
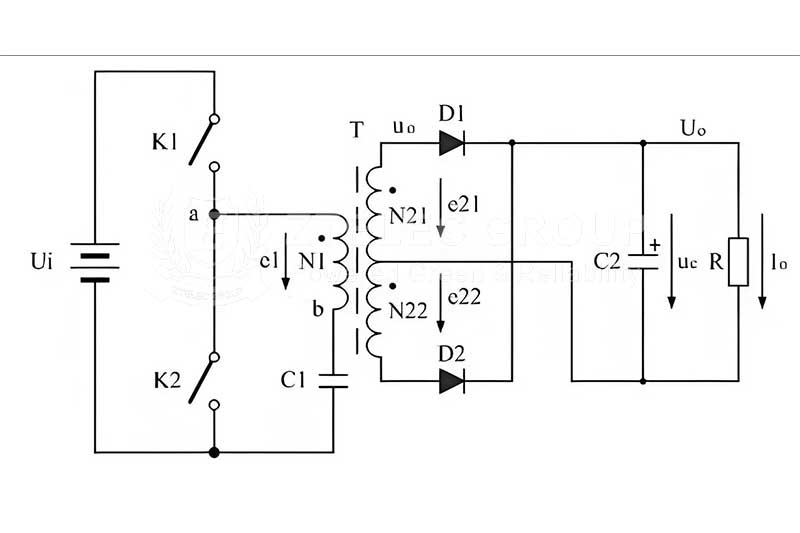
Transformers and switching power supplies play different roles in power transmission. Transformers are crucial for the efficient distribution of electricity in power systems, while switching power supplies are ubiquitous in powering modern electronic devices. Understanding their basic principles and respective advantages not only enables us to apply these technologies better, promoting optimization and innovation in power systems, but also reveals the mysteries of power transmission. In the future, the combination and innovative applications of both will further advance power transmission technology to meet the ever-growing demand for electricity, as well as in energy management and green energy development.
- more+releated article
- 2026-01-04Common Power Transformer Faults: Causes, Solut
- 2025-12-312026 New Year Holiday Notice
- 2025-12-31Operation, Maintenance, and Service Life Manag
- 2025-12-30How to Select a 100 kVA–500 kVA Distribution
- 2025-12-29The Impact of NHN NMN Composite Insulation on
- 2025-12-26Practical Application of GPO-3 Insulation Boar
- 2025-12-2510kV Transformer Replacement Timeline: Install
- 2025-12-25Low Smoke EN45545 GPO3 UPGM203 Laminated Board
- 2025-12-24Merry Christmas — ZTelecgroup Christmas Cele
- 2025-12-24How to Select a Suitable 50kVA–500kVA Distri






