G10 Machined Part Production Process Analysis: Quality Control from Materials to Finished Product
G10 machined parts, as high-performance composite materials, are widely used in various fields, including electronics, machinery, and aerospace. Their excellent insulation, mechanical strength, and environmental resistance make them a crucial component of many critical devices. Achieving these superior properties requires precise control at every stage of production, from raw materials to finished product. Below, we will detail the G10 machined part production process and explore how quality control at each stage ensures product quality.
1. Raw Material Preparation for G10 Machined Parts
Material Composition
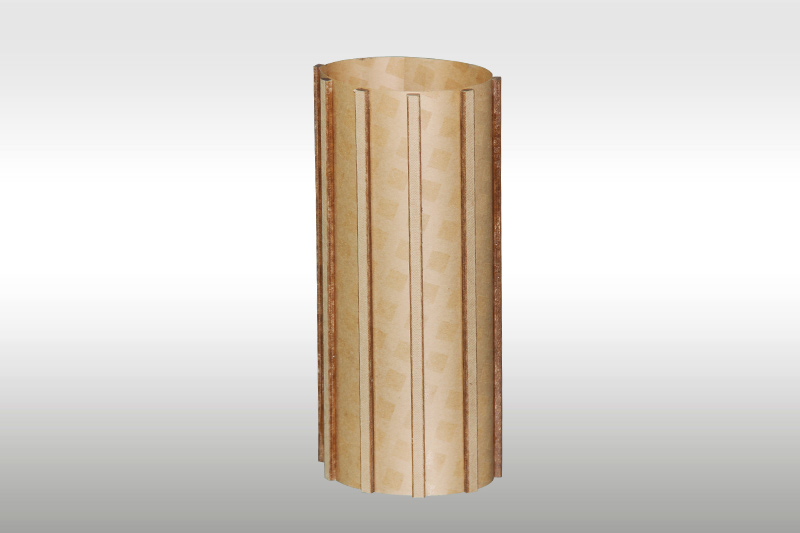
The core materials of G10 machined parts are epoxy resin and fiberglass cloth. The purity and viscosity of epoxy resin directly affect the final performance of the epoxy board, while the density and structural strength of the fiberglass cloth are also key factors affecting product quality.
Raw Material Selection
The raw materials for G10 machined parts are selected based on the specific requirements of the product. For example, for laminates requiring strong physical properties, specialized raw materials are used; for laminates requiring excellent performance in electrical equipment, other materials are used. Mixing and Impregnation
When impregnating the fiberglass cloth with epoxy resin, uniform impregnation is crucial. This ensures that the epoxy resin fully penetrates every gap in the cloth. Process conditions during this step, such as impregnation time and ambient temperature, must be strictly controlled.
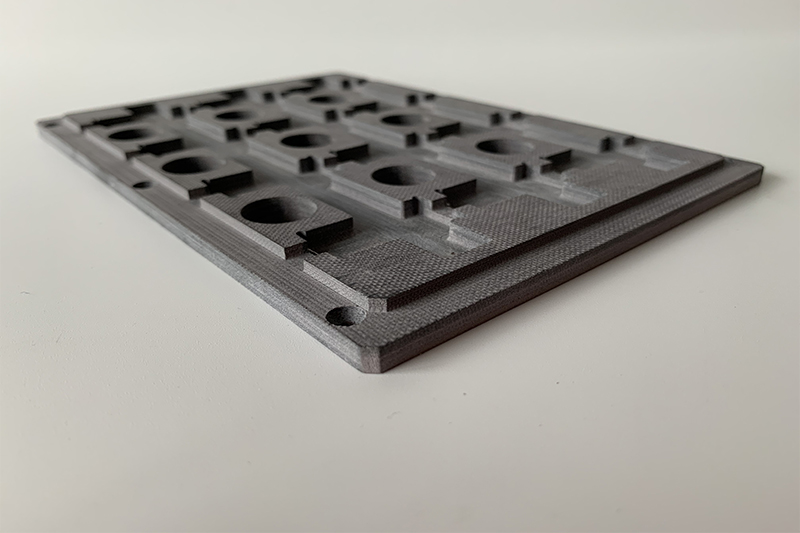
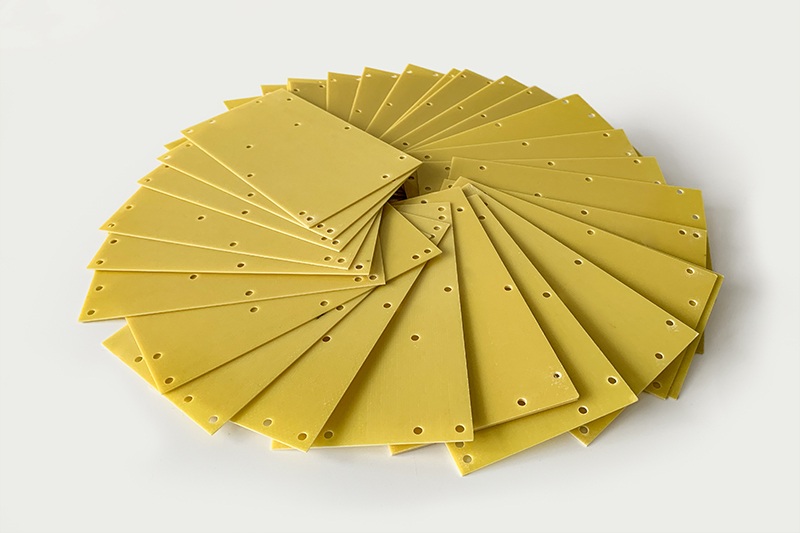
2.G10 Part Forming Stage
Molding Process
Molding processes include hot pressing, cold pressing, and injection molding. During the molding process, the material's density, thickness, and dimensional accuracy must meet established standards to ensure the performance and quality of the finished product meet standards.
Lamination Process
The impregnated fiberglass cloth is laminated according to the specified number of layers and orientation. The pressure, temperature, and duration of the lamination process are important control factors, directly affecting the density, structural strength, and insulation properties of the epoxy board.

3.G10 Machined Part Machining Process
Equipment: High-precision CNC machines equipped with carbide or diamond tools are used.
Key Processes
Drilling: Utilize a low-speed mode combined with a pecking drill process to effectively prevent fiber edge chipping.
Milling: Utilize down-cut milling to minimize material delamination. Use deionized water or specialized cutting fluid as coolant.
Cutting: Laser cutting is suitable for machining complex contours, but effective control of the heat-affected zone is essential.
Quality Inspection Points
Dimensional Accuracy: Measured using a three-dimensional coordinate measuring machine to ensure compliance with required tolerances.
Edge Quality: Microscopically inspected to ensure the absence of delamination and burrs.
Deburring and Chamfering: Sharp edges are chamfered to a smooth finish using either manual or mechanical polishing (using 400# sandpaper or higher).

4.G10 Part Surface Treatment (As Needed)
Cleaning
Use ultrasonic cleaning (using isopropyl alcohol or a neutral detergent) to thoroughly remove surface dust and oil.
Special Treatments
Anti-Arc Coating: Apply an insulating varnish (such as polyurethane) by spraying. After curing, test the coating thickness.
Metallization: Use electroless copper plating or immersion gold plating. This treatment is primarily used for PCB connectors.
5.Inspection and Testing
Electrical Performance Testing:
Insulation resistance testing and breakdown voltage testing are performed to ensure that the electrical performance of the machined part meets the required performance.
Mechanical Performance Testing:
Tensile strength testing, flexural strength testing, and impact toughness testing are performed to comprehensively evaluate the mechanical performance of the machined part.
Environmental Adaptability Testing:
Simulate various environmental conditions, such as salt spray, high temperature, and high humidity, to verify the machined part's environmental resistance in different environments.
The production of G10 machined parts is a highly integrated process, from the careful selection and mixing of raw materials, to process control during the molding stage, machining, surface treatment, and final inspection and testing. Each step plays a crucial role in product quality. Only by strictly controlling quality at every stage of the production process can we ensure the stable and reliable performance of G10 machined parts, meet the high standards required by various industries, and provide a solid foundation for the safe and stable operation of related equipment.
- more+releated article
- 2025-10-21Application of K Factor Transformer
- 2025-10-21Detailed explanation about transformer model w
- 2025-10-2010kV Oil-Immersed Transformer Safety: Lightnin
- 2025-10-20What are The Advantages of Phenolic Cotton Clo
- 2025-10-17Are Three-Phase Isolation Dry-Type Transformer
- 2025-10-17G10 Epoxy Sheet: Choosing the Right Specificat
- 2025-10-1610kV Oil-Immersed Transformer Operation Inspec
- 2025-10-163240-B Epoxy Phenolic Glass Fiber Cloth Lamina
- 2025-10-15G10 Epoxy Sheet: The Preferred Insulation Mate
- 2025-10-15Analysis of Energy-Saving and Noise Control Te





