What is FR-4 Glass Epoxy Laminate material
2024-06-28 12:20 | By: ZTELEC-www.ztelecgroup.com | 156click
what is fr4
FR4, which stands for Flame Retardant 4, is a NEMA grade designation for glass-reinforced epoxy laminate material. It’s a composite material composed of woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder that is flame resistant (self-extinguishing). The “FR” indicates that the material is flame retardant, and it’s known for its high mechanical values and electrical insulating qualities in both dry and humid conditions.
FR4 is most commonly used as an electrical insulator possessing considerable mechanical strength, making it a popular choice for a wide variety of electrical and mechanical applications. It’s also the material of choice for the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs) due to its durability, excellent electrical properties, and thermal stability

FR-4 date
It seems you’re asking about the release date for FR4 material. FR4 has been a standard material in the electronics industry for many years, and its exact “release date” isn’t typically specified as it’s not a product with a launch date like software or consumer electronics.
However, if you’re referring to a specific product or version of FR4 material, such as a new formulation or variant, I would need more context to provide an accurate answer. For general information, FR4 has been in use since the development of PCBs and has become the standard due to its reliable properties and performance in various applications.
If you’re looking for the release date of a software or product named “FR4,” I would need additional details to assist you further. Please provide more information or clarify your request so I can help you effectively.
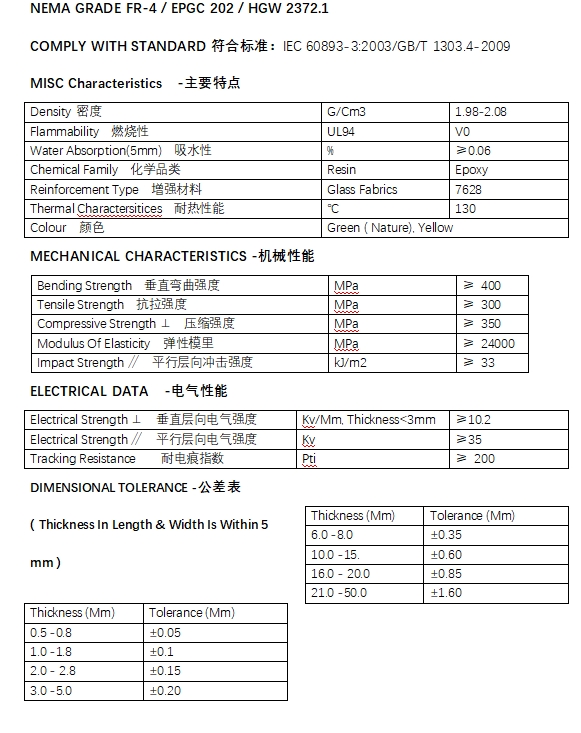
FR-4 material properties
FR-4 is a widely used material with a set of properties that make it ideal for various applications, especially in the electronics industry. Here’s a concise summary of FR-4 material properties:
Density: 1.850 g/cm³1
Water Absorption: Less than 0.10%
Temperature Index: 140°C (284°F)
Thermal Conductivity:
Through-plane: 0.29 W/(m·K)
In-plane: 0.81 W/(m·K)
Flexural Strength:
Lengthwise (LW): > 415 MPa
Crosswise (CW): > 345 MPa
Dielectric Breakdown: > 50 kV
Relative Permittivity (Dielectric Constant): 4.4
These properties contribute to FR-4’s excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and flame retardancy, making it a preferred choice for printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other electrical insulation applications
Difference between FR-4 and fr-5
FR-4 and FR-5 are both flame-retardant glass epoxy laminate materials used in the construction of printed circuit boards (PCBs), but they have some differences, primarily in their temperature resistance and mechanical properties at higher temperatures. Here’s a comparison:
FR-4:
Composition: Woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with an epoxy resin.
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg): Generally around 130-140°C. This is the temperature at which the material transitions from a rigid to a more flexible state.
Applications: Suitable for a broad range of standard electronic applications, including consumer electronics and general-purpose PCBs.
FR-5:
Composition: Similar to FR-4, it’s made of woven fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin. The difference lies in the resin formulation, which gives FR-5 its unique properties.
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg): Higher than FR-4, often around 150-170°C or even higher, which makes it suitable for applications requiring higher temperature resistance.
Applications: Often chosen for high-frequency and high-speed communication devices, military applications, and other specialized electronics that operate under harsh conditions.
The primary difference is the higher Tg rating of FR-5, which provides improved functionality compared to FR-4 due to superior mechanical properties at raised temperatures, both in humid and dry conditions. The choice between FR-4 and FR-5 will depend on the specific needs of the project, considering factors like operating temperature, mechanical strength, and cost
FR-4 is different from g10
Yes, FR4 and G10 are both glass epoxy composite materials, but they differ mainly in their flame-retardant properties. Here’s a brief comparison:
FR4:
Flame Retardant: Contains a bromine compound that makes it compliant with the UL standard 94V-0 for flame resistance.
Applications: Primarily used in the electronics industry for printed circuit boards (PCBs) due to its flame retardancy and excellent electrical insulation properties.
G10:
Non-Flame Retardant: Does not contain flame-retardant additives and is not rated for flame resistance.
Strength in Salt Water: G10 outperforms FR4 in applications immersed in salt water, making it suitable for certain marine applications.
Applications: Known for its high mechanical strength and excellent dielectric properties, G10 is used in various industries, including electronics and aerospace.
While both materials have similar mechanical and electrical properties, the key difference lies in their use in environments where flame retardancy is either required or not. FR4’s flame resistance makes it more suitable for applications where fire safety is a concern, whereas G10’s lack of flame-retardant additives can be advantageous in certain specialized applications
FR-4 fabrication
The fabrication process of FR-4 material involves several steps that are standard in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Here’s a concise overview of the key stages:
Laminating: The process starts with the lamination of epoxy resin and woven glass fiber cloth to create the FR-4 sheets.
Drilling: Once the sheets are prepared, precise holes are drilled as per the PCB design to place electronic components.
Circuit Patterning: A photoresist is applied to the FR-4, and then it is exposed to light through a mask to create the circuit pattern.
Etching: The exposed FR-4 is then subjected to chemical etching to remove unwanted copper, leaving behind the desired circuit traces.
Solder Mask Application: A solder mask is applied over the FR-4 to protect the copper circuits and prevent solder bridging during component placement.
Component Assembly: Electronic components are placed onto the prepared FR-4 board and soldered in place, either manually or by automated processes.
Testing and Inspection: The completed PCB is tested for functionality and inspected for any defects.
FR-4 is compatible with these standard PCB fabrication processes, which simplifies manufacturing and helps reduce production costs. Its properties, such as flame retardancy and mechanical strength, ensure reliability throughout the manufacturing process and in the final electronic applications.
Advantages and disadvantages of FR-4
FR-4 is a popular material in the electronics industry, particularly for printed circuit boards (PCBs). Here are the advantages and disadvantages of FR-4:
Advantages:
High Strength and Rigidity: The woven fiberglass cloth provides high tensile strength, making FR-4 resistant to bending and breaking.
Excellent Electrical Insulation: The epoxy resin acts as an insulator, preventing electrical current from flowing through the material.
Good Thermal Stability: FR-4 can withstand high temperatures without degrading, which is beneficial for devices that generate heat.
Low Water Absorption: Its resistance to moisture and humidity makes it suitable for devices exposed to harsh environments.
Disadvantages:
High Cost: The materials used to make FR-4 are expensive, which can increase the overall cost of the final product.
Difficult to Work With: FR-4’s hardness and brittleness can make it challenging to cut and drill during manufacturing.
Limited Flexibility: Its rigidity can be a drawback when flexibility is required in the design of electronic devices.
Hazardous Waste: The materials used in FR-4 can be toxic and harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly.
These factors should be considered when choosing FR-4 for electronic applications to ensure it meets the specific needs and compliances of the product.
applications for FR-4 material
FR-4 material is extensively used in various industries due to its excellent mechanical and electrical properties. Here are some common applications:
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): FR-4 is the primary material used for PCBs in electronic devices due to its dielectric properties, thermal resistance, and mechanical strength.
Electrical Insulators: Its high electrical insulation makes it suitable for use as an insulator in transformers, electric motors, and other electrical equipment.
Communication Devices: FR-4 is used in the manufacturing of components for communication devices such as antennas, signal amplifiers, and routers.
Computer Hardware: It is found in computer motherboards, power supplies, and other internal hardware components.
Consumer Electronics: FR-4 is used in a variety of consumer electronics, including smartphones, televisions, and home appliances.
Industrial Electronics: The material’s durability and resistance to harsh environments make it ideal for industrial control systems.
Medical Devices: FR-4’s reliability and safety features are beneficial in medical electronic devices like imaging equipment and patient monitoring systems.
These applications benefit from FR-4’s flame retardancy, stability, and reliability, making it a cornerstone material in the electronics industry
Price of FR-4
The price of FR-4 material can vary based on several factors such as thickness, copper cladding, surface finish, and the quantity ordered. Generally, the cost ranges from a few dollars per square foot for standard FR-4 material to higher prices for specialized variants or custom specifications.
For specific applications that require high-temperature resistance, High-TG FR-4 PCBs are available. These are designed to withstand higher operating temperatures and have a glass transition temperature (Tg) value of up to 180°C. The price for these high-TG PCBs will be higher due to their enhanced properties.
If you’re looking to purchase FR-4 material for your projects, it’s best to get a quote from suppliers like PCBCart, which offers a range of high-temperature PCB products and can provide customized boards to meet specific demands. Keep in mind that bulk orders typically reduce the cost per unit, so consider your volume needs when inquiring about prices.Of course, you can also contact us manufacturers directly

tags:insulation failure transformertransformer short circuittransformer overheatingtransformer overloadtransformer maintenance
- more+releated article
- 2026-01-04Common Power Transformer Faults: Causes, Solut
- 2025-12-312026 New Year Holiday Notice
- 2025-12-31Operation, Maintenance, and Service Life Manag
- 2025-12-30How to Select a 100 kVA–500 kVA Distribution
- 2025-12-29The Impact of NHN NMN Composite Insulation on
- 2025-12-26Practical Application of GPO-3 Insulation Boar
- 2025-12-2510kV Transformer Replacement Timeline: Install
- 2025-12-25Low Smoke EN45545 GPO3 UPGM203 Laminated Board
- 2025-12-24Merry Christmas — ZTelecgroup Christmas Cele
- 2025-12-24How to Select a Suitable 50kVA–500kVA Distri





