High Voltage Verses Low Voltage Transformers
In modern power systems, transformers serve as an important electrical device, playing a crucial role in the transmission and distribution of electrical energy. There are various types of transformers, among which high voltage transformers and low voltage transformers are the most common. This article will compare and analyze high voltage transformers and low voltage transformers, exploring their structural characteristics, operating principles, application fields, and their significance in power systems.
Definition and Characteristics of High Voltage Transformers
A high voltage transformer is a type of power transformer that operates at high voltages (generally considered to be over 1000 volts). Its primary function is to convert electrical energy from power plants or high voltage transmission lines into voltage levels suitable for consumer use. High voltage transformers typically consist of components such as the transformer core, windings, insulation system, and oil tank. The core is usually made of high-quality silicon steel sheets to minimize energy loss. Additionally, the winding materials are generally high-conductivity copper or aluminum to enhance the efficiency of the transformer.
High voltage transformers are characterized by high efficiency, low losses, and high voltage tolerance. During long-distance transmission, high voltage transformers can effectively reduce power losses in the lines, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the power system.
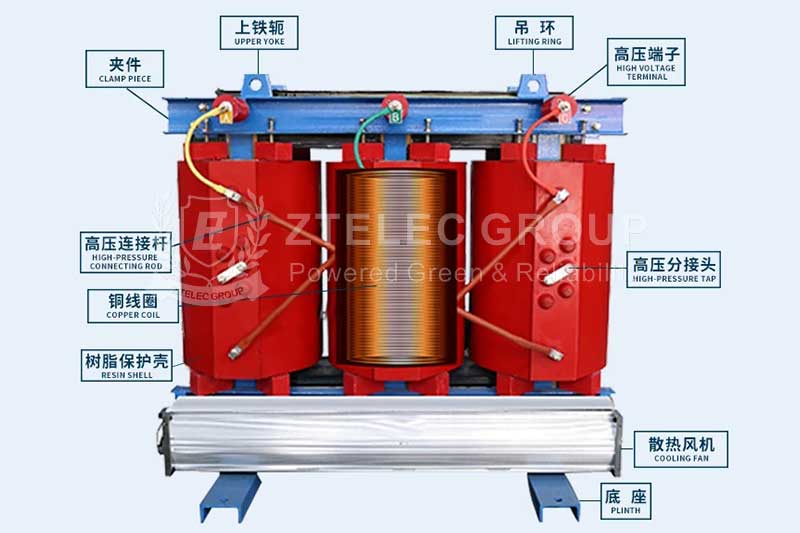

Definition and Characteristics of Low Voltage Transformers
In contrast to high voltage transformers, low voltage transformers are primarily used for electrical conversion at lower voltages (generally considered to be below 1000 volts). Their main function is to further convert electrical energy from medium voltage distribution networks into low voltage electrical energy that is safe and suitable for household and commercial use. Low voltage transformers also consist of a core, windings, insulation materials, etc., but their structure is relatively simple and smaller in size.
Low voltage transformers are commonly used to power various electrical devices, offering advantages such as high safety, convenience, and low maintenance costs. Although their application range in voltage levels is limited, low voltage transformers still play an essential role in daily life and industrial production.
Operating Principles of High Voltage Transformers and Low Voltage Transformers
Although high voltage transformers and low voltage transformers differ in voltage levels and application fields, their operating principles are similar, both based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The operation of a transformer can be divided into two main stages: the input stage and the output stage.
In the input stage, when alternating current flows through the primary winding of the high voltage transformer, it generates a changing magnetic field, which produces magnetic flux in the core. The change in magnetic flux further induces voltage in the secondary winding. According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, the magnitude of the voltage is related to the ratio of the number of turns in the windings. Therefore, by changing the turns ratio between the primary and secondary windings, the transformer can achieve voltage increase or decrease.
In the output stage, the voltage induced in the secondary winding is delivered to the load, completing the entire process of electrical energy conversion. In high voltage transformers, the number of turns in the secondary winding is usually less than that in the primary winding, thereby achieving voltage reduction. Conversely, in low voltage transformers, the primary winding typically has fewer turns while the secondary winding has more turns, resulting in voltage increase.

Low Voltage Transformers
Application Fields of High Voltage Transformers and Low Voltage Transformers
The application fields of high voltage transformers and low voltage transformers differ significantly. High voltage transformers are mainly used in power transmission systems, including power plants, substations, and high voltage transmission lines. In long-distance transmission and multiple load connections, high voltage transformers can effectively reduce transmission losses, ensuring the stability and reliability of power supply.
In contrast to high voltage transformers, low voltage transformers are more closely related to everyday life. They are widely used in the power supply of household appliances, commercial equipment, and industrial production. Low voltage transformers not only supply power for general lighting, computers, and household appliances but are also commonly used for medical devices, communication equipment, and power conversion in specific scenarios.
Importance of High Voltage Transformers and Low Voltage Transformers in Power Systems
High voltage transformers and low voltage transformers each play an indispensable role in power systems. High voltage transformers ensure the efficient transmission of electrical power, allowing energy to flow smoothly from generation sources to various consumption points, providing essential energy support for daily life in cities and rural areas. Their presence also reduces energy losses due to distance in large-scale power supply processes, improving the economic efficiency of the power system.
Low voltage transformers, on the other hand, are closer to civilian life, providing a safe and reliable electrical environment. By converting medium voltage electrical energy into low voltage power, low voltage transformers ensure the safety of residential electricity use and the normal operation of various electrical devices. Particularly in modern society, the role of low voltage transformers is becoming increasingly important, as they directly affect people's quality of life and production efficiency.
High voltage transformers and low voltage transformers each hold significant positions and functions in power systems. The former is responsible for long
1250kVA oil immersed transformer price
1600kVA oil immersed transformer
FR4 Machined Parts
1250kVA oil immersed transformer
Filament Wound Epoxy Tube
- more+releated article
- 2026-02-281250kVA Oil-Immersed Transformer Price and Cos
- 2026-02-27Detailed Explanation of FR4 Machined Parts Mac
- 2026-02-27Custom 1600kVA Oil Immersed Transformer Manufa
- 2026-02-26Precision FR4 Machined Parts for Electrical In
- 2026-02-26High-Quality Industrial 1250kVA Oil-Immersed T
- 2026-02-25Why is Filament Wound Epoxy Tube More Expensiv
- 2026-02-25XUJUE ELECTRICAL Officially Resumes Operations
- 2026-02-25Solar Duty Transformer: Sizing Challenges, Inv
- 2026-02-11Ztelecgroup Annual Gala Successfully Held
- 2026-02-10G10 epoxy board in the insulation parts of ele